absorbers--Dark-colored objects that soak up heat in thermal solar collectors.
active solar heater--A solar water or space-heating system that moves heated air or water using pumps or fans.
AGM -- Absorbed Glass Mat, a newer type of battery construction that uses saturated absorbent glass mats rather than gelled or liquid electrolyte. Somewhat more expensive than flooded (liquid), but offers very good reliability.
alternating current--Electric current in which the direction of flow is reversed at frequent intervals--usually 100 or 120 times per second (50 or 60 cycles per second or 50//60 Hz).
amorphous semiconductor--A non-crystalline semiconductor material. Easier and cheaper to make than crystalline, but less efficient and slowly degrades over time. Also called thin film.
ampere (A) or amp--The unit for the electric current; the flow of electrons. One amp is 1 coulomb passing in one second. One amp is produced by an electric force of 1 volt acting across a resistance of 1 ohm.
ampere-hour (AH)--Quantity of electricity or measure of charge. How many amps flow or can be provided over a one hour period. Most batteries are rated in AH.
angle of incidence--Angle between the normal to a surface and the direction of incident radiation; applies to the aperture plane of a solar collector. Most modern solar panels have only minor reductions in power output within plus/minus 15 degrees. The loss is a function of the cosine, so at 45 degree angle, output drops off by about 30%.
antireflection coating--A thin coating of a material, which reduces the light reflection and increases light transmission, applied to a photovoltaic cell surface.
array--Any number of photovoltaic modules connected together to provide a single electrical output. Arrays are often designed to produce significant amounts of electricity.
autonomous system--A stand-alone PV system that has no back-up generating source. May or may not include storage batteries. Most battery systems are designed for a certain minimum "days of autonomy" - which means that the batteries can supply sufficient power with no sunlight to charge the batteries. This varies from 3-5 days in the sunbelt, to 5 to 10 days elsewhere.
AWG -- American Wire Gauge, a standard system for designating the size of electrical wire. The higher the number, the smaller the wire. Most house wiring is #12 or 14. In most other countries, wire is specified by the size in millimeters.
azimuth--Angle between the north direction and the projection of the surface normal into the horizontal
plane; measured clockwise from north. As applied to the PV array, 180 degree azimuth means the array faces due south.
balance of system (BOS)--Represents all components and costs other than the PV modules. It includes design costs, land, site preparation, system installation, support structures, power conditioning, operation and maintenance costs, batteries, indirect storage, and related costs.
baseline performance value--Initial values of Isc, Voc, Pmp, Imp measured by the accredited laboratory and corrected to Standard Test Conditions, used to validate the manufacturer's performance measurements provided with the qualification modules per IEEE 1262.
blocking diode--A diode used to restrict or block reverse current from flowing backward through a module. [UL 1703] Alternatively, diode connected in series to a PV string; it protects its modules from a reverse power flow and, thus, against the risk of thermal destruction of solar cells.
British thermal unit (BTU)--The amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one pound of water from 60 degrees F to 61 degrees F at one atmosphere pressure.
bypass diode--A diode connected across one or more solar cells in a photovoltaic module such that the diode will conduct if the cell(s) become reverse biased. [UL 1703] Alternatively, diode connected anti-parallel across a part of the solar cells of a PV module. It protects these solar cells from thermal destruction in case of total or partial shading, broken cells, or cell string failures of individual solar cells while other cells are exposed to full light.
cathodic protection--A method of preventing oxidation (rusting) of exposed metal structures, such as bridges and pipelines, by imposing between the structure and the ground a small electrical voltage that opposes the flow of electrons and that is greater than the voltage present during oxidation.
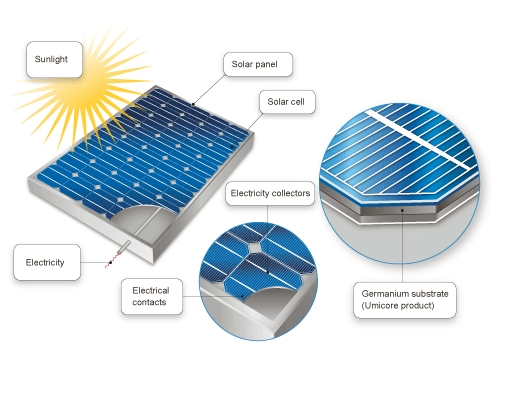
cell--The basic unit of a photovoltaic panel or battery
cell barrier--A very thin region of static electric charge along the interface of the positive and negative layers in a photovoltaic cell. The barrier inhibits the movement of electrons from one layer to the other, so that higher-energy electrons from one side diffuse preferentially through it in one direction, creating a current and thus a voltage across the cell. Also called depletion zone, cell junction, or space charge.
cell junction--The area of immediate contact between two layers (positive and negative) of a photovoltaic cell. The junction lies at the center of the cell barrier or depletion zone.
charge controller--An electronic device which regulates the voltage applied to the battery system from the PV array. Essential for ensuring that batteries obtain maximum state of charge and longest life.
combined collector--A photovoltaic device or module that provides useful heat energy in addition to electricity.
concentrator--A PV module that uses optical elements to increase the amount of sunlight incident on a PV cell. Concentrating arrays must track the sun and use only the direct sunlight because the diffuse portion cannot be focused onto the PV cells. Efficiency is increased, but lifespan is usually decreased due to the high heat.
concentrator (module, array, or collector)--An arrangement of photovoltaic cells that includes a lens to concentrate sunlight onto small-area cells. Concentrators can increase the power flux of sunlight hundreds of times.
conversion efficiency (cell or module)--The ratio of the electric energy produced by a photovoltaic device (under one-sun conditions) to the energy from sunlight incident upon the cell.
current at maximum power (Imp)--The current at which maximum power is available from a module. [UL 1703]
cycle life--Number of discharge-charge cycles that a battery can tolerate under specified conditions before it fails to meet specified criteria as to performance (e.g., capacity decreases to 80-percent of the nominal capacity).
dc to dc converter--Electronic circuit to convert dc voltages (e.g., PV module voltage) into other levels (e.g., load voltage). Can be part of a maximum power point tracker (MPPT).
deep discharge--Discharging a battery to 20-percent or less of its full charge.
diffuse insolation--Sunlight received indirectly as a result of scattering due to clouds, fog, haze, dust, or other obstructions in the atmosphere. Opposite of direct insolation.
direct current (dc)--Electric current in which electrons flow in one direction only. Opposite of alternating current.
direct insolation--Sunlight falling directly upon a collector. Opposite of diffuse insolation.
discharge rate--The rate, usually expressed in amperes or time, at which electrical current is taken from the battery.
distributed systems--Systems that are installed at or near the location where the electricity is used, as opposed to central systems that supply electricity to grids. A residential photovoltaic system is a distributed system.
DOD--'Depth of Discharge,' from 100-percent state of charge (SOC), in a battery or battery system.
electric circuit--Path followed by electrons from a power source (generator or battery) through an external line (including devices that use the electricity) and returning through another line to the source.
electric current--A flow of electrons; electricity, amps.
electrical grid--An integrated system of electricity distribution, usually covering a large area. As in "off the grid".
electrolyte--A liquid conductor of electricity. In batteries, usualy H2SO4, sulfuric acid, but may be any number of things. Seawater is the most common electrolyte in the world - and by suspending a zinc and a steel sheet in it, you can get a little electricity.
energy--The ability to do work. Stored energy becomes working energy when we use it.
energy density--The ratio of energy available from a battery to its volume (Wh/1) or mass (Wh/kg). "watts to weight" ratio.
energy payback time--The time required for any energy producing system or device to produce as much
energy as was required in its manufacture. For solar electric panels, this is about 16-20 months.
EVA--(ETHYLENE VINYL ACETATE) An encapsulant used between the glass cover and the solar cells in PV modules. It is durable, transparent, resistant to corrosion, and flame retardant.
flat-plate PV--Refers to a PV array or module that consists of nonconcentrating elements. Flat-plate arrays and modules use direct and diffuse sunlight, but if the array is fixed in position, some portion of the direct sunlight is lost because of oblique sun-angles in relation to the array.
float charge--Float charge is the voltage required to counteract the self-discharge of the battery at a certain temperature.
float life--Number of years that a battery can keep its stated capacity when it is kept at float charge (see float charge).
fuel cell--A device that converts the energy of a fuel directly to electricity and heat, without combustion. Because there is no combustion, fuel cells give off few emissions; because there are no moving parts, fuel cells are quiet.
gel-type battery--Lead-acid battery in which the electrolyte is composed of a silica gel matrix.
grid-connected (PV system)--A PV system in which the PV array acts like a central generating plant, supplying power to the grid.
ground loop--An undesirable feedback condition caused by two or more circuits sharing a common electrical line, usually a grounded conductor.
hot spot--An undesirable phenomenon of PV device operation whereby one or more cells within a PV
module or array act as a resistive load, resulting in local overheating or melting of the cell(s).
hybrid system--A PV system that includes other sources of electricity generation, such as wind or fossil fuel generators.
incident light--Light that shines onto the face of a solar cell or module.
insolation--Sunlight, direct or diffuse; from 'incident solar radiation.' Not to be confused with 'insulation.' Equal to about 1000 watts per square meter at high noon in Dodge City.
interconnect--A conductor within a module or other means of connection which provides an electrical interconnection between the solar cells. [UL 1703]
inverters--Devices that convert dc electricity into ac electricity (single or multiphase), either for stand-alone systems (not connected to the grid) or for utility-interactive systems.
I-V curve--A graphical presentation of the current versus the voltage from a photovoltaic device as the load is increased from the short circuit (no load) condition to the open circuit (maximum voltage) condition. The shape of the curve characterized cell performance.
I-V data--The relationship between current and voltage of a photovoltaic device in the power-producing quadrant, as a set of ordered pairs of current and voltage readings in a table, or as a curve plotted in a suitable coordinate system (i.e., Cartesian). [ASTM E 1036]
junction box--A PV generator junction box is an enclosure on the module where PV strings are electrically connected and where protection devices can be located, if necessary.
junction diode--A semiconductor device with a junction and a built-in potential that passes current better in one direction than the other. All solar cells are junction diodes.
kilowatt (kW)--1000 watts.
kilowatt-hour (kWh)--One thousand watts acting over a period of 1 hour. The kWh is a unit of energy. 1 kWh=3600 kJ.
light-induced defects--Defects, such as dangling bonds, induced in an amorphous silicon semiconductor upon initial exposure to light.
light trapping--The trapping of light inside a semiconductor material by refracting and reflecting the light at critical angles; trapped light will travel further in the material, greatly increasing the probability of absorption and hence of producing charge carriers.
line-commutated inverter--An inverter that is tied to a power grid or line. The commutation of power (conversion from dc to ac) is controlled by the power line, so that, if there is a failure in the power grid, the PV system cannot feed power into the line.
load--Anything in an electrical circuit that, when the circuit is turned on, draws power from that circuit.
maximum power point (MPP)--The point on the current-voltage (I-V) curve of a module under illumination, where the product of current and voltage is maximum. [UL 1703] For a typical silicon cell panel, this is about 17 volts for a 36 cell configuration.
maximum power point tracker (MPPT)--A power conditioning unit that automatically operates the PV-generator at its maximum power point under all conditions. An MPPT will typically increase power delivered to the system by 10% to 40%, depending on climate conditions and battery state of charge. You usually get more gain in winter and in colder weather due to the higher panel output. Most MPPT controllers are down converters - from a higher voltage to a lower one.
microgroove--A small groove scribed into the surface of a cell which is filled with metal for contacts.
module--A number of PV cells connected together, sealed with an encapsulant, and having a standard size and output power; the smallest building block of the power generating part of a PV array. Also called panel.
monolithic--Fabricated as a single structure.
multicrystalline--Material that is solidified at such as rate that many small crystals (crystallites) form. The atoms within a single crystallite are symmetrically arranged, whereas crystallites are jumbled together. These numerous grain boundaries reduce the device efficiency. A material composed of variously oriented, small individual crystals. (Sometimes referred to as polycrystalline or semicrystalline).
multijunction device--A photovoltaic device containing two or more cell junctions, each of which is optimized for a particular part of the solar spectrum, to achieve greater overall efficiency.
n-type semiconductor--A semiconductor produced by doping an intrinsic semiconductor with an electron-donor impurity (e.g., phosphorous in silicon).
NOCT--Nominal Operating Cell Temperature. The solar cell temperature at a reference environment defined as 800 W/m2 irradiance, 20°C ambient air temperature, and 1 m/s wind speed with the cell or module in an electrically open circuit state.
ohm--The unit of resistance to the flow of an electric current.
one-axis tracking--A system capable of rotating about one axis, usually following the sun from East to West.
open-circuit voltage (Voc)--The maximum possible voltage across a photovoltaic cell or module; the voltage across the cell in sunlight when no current is flowing.
parallel connection--A way of joining two or more electricity-producing devices (i.e., PV cells or modules) by connecting positive leads together and negative leads together; such a configuration increases the current.
passive solar home--A house that uses a room or another part of the building as a solar collector, as opposed to active solar, such as PV.
peak load; peak demand--The maximum load, or usage, of electrical power occurring in a given period of time, typically a day.
peak watts (Wp)--See 'Photovoltaic peak watt.'
photon--A particle of light that acts as an individual unit of energy.
photovoltaic (PV)--Pertaining to the direct conversion of light into electricity.
photovoltaic (PV) array--An interconnected system of PV modules that function as a single electricity-producing unit. The modules are assembled as a discrete structure, with common support or mounting. In smaller systems, an array can consist of a single module.
photovoltaic (PV) cell--The smallest semiconductor element within a PV module to perform the immediate conversion of light into electrical energy (dc voltage and current).
photovoltaic (PV) conversion efficiency--The ratio of the electric power produced by a photovoltaic device to the power of the sunlight incident on the device.
photovoltaic (PV) efficiency--The ratio of electric power produced by a cell at any instant to the power of the sunlight striking the cell. This is typically about 9% to 14% for commercially available cells.
photovoltaic (PV) generator--The total of all PV strings of a PV power supply system, which are electrically interconnected.
photovoltaic (PV) module--The smallest environmentally protected, essentially planar assembly of solar cells and ancillary parts, such as interconnections, terminals, [and protective devices such as diodes] intended to generate DC power under unconcentrated sunlight. The structural (load carrying) member of a module can either be the top layer (superstrate) or the back layer (substrate). [UL 1703]
photovoltaic (PV) panel--often used interchangeably with PV module (especially in one-module systems), but more accurately used to refer to a physically connected collection of modules (i.e., a laminate string of modules used to achieve a required voltage and current).
photovoltaic (PV) peak watt--Maximum "rated" output of a cell, module, or system. Typical rating conditions are 0.645 watts per square inch (1000 watts per square meter) of sunlight, 68 degrees F (20 degrees C) ambient air temperature and 6.2 x 10-3 mi/s (1 m/s) wind speed.
photovoltaic (PV) system--A complete set of components for converting sunlight into electricity by the photovoltaic process, including the array and balance of system components.
photovoltaic-thermal (PV/T) system--A photovoltaic system that, in addition to converting sunlight into electricity, collects the residual heat energy and delivers both heat and electricity in usable form. Also called a total energy system.
polycrystalline--See 'Multicrystalline.'
power conditioning equipment--Electrical equipment, or power electronics, used to convert power from a photovoltaic array into a form suitable for subsequent use. A collective term for inverter, converter, battery charge regulator, and blocking diode.
power factor--The ratio of the average power and the apparent volt-amperes. Affected by the inductance and capacitance of the load. A pure resistance, such as an electric heater would have a power factor of 1.00.
pulse-width-modulated (PWM) - A function of many of the newer charge controllers and battery chargers which instead of applying a steady DC voltage to the battery, sends out short pulses. The width of the pulses varies with the battery state of charge.
PV--Abbreviation for photovoltaic(s).
pyronometer--An instrument for measuring total hemispherical solar irradiance on a flat surface, or "global"
irradiance; thermopile sensors have been generally identified as pyranometers,however, silicon sensors are
also referred to as pyranometers.
qualification test (PV)--A procedure applied to a selected set of PV modules involving the application of defined electrical, mechanical, or thermal stress in a prescribed manner and amount. Test results are subject to a list of defined requirements.
rectifier--A device that converts ac to dc, as in a battery charger or converter. See inverter and diode.
remote systems--Systems off of the utility grid. Out in the boondocks.
resistive voltage drop--The voltage developed across a cell by the current flow through the resistance of the cell.
reverse bias--Condition where the current producing capability of a PV cell is significantly less than that of other cells in its series string. This can occur when a cell is shaded, cracked, or otherwise degraded or when it is electrically poorly matched with other cells in its string.
Schottky barrier--A cell barrier established as the interface between a semiconductor, such as silicon, and a sheet of metal.
Schottky diode - a special diode with a very low voltage drop, usually in the .15 to .25 volt range. Often used as blocking diodes in solar panels and arrays to minimize power loss. A normal silicon diode drops at least .7 volts.
self discharge--The rate at which a battery, without a load, will lose its charge. This can vary considerably depending on the type of battery and age. It can be as low as 3% a month for a new AGM battery, and as high as 10% a week for an older Lead-Antimony (industrial) battery.
semiconductor--Any material that has a limited capacity for conducting an electric current. Generally falls between a metal and an insulator in conductivity. Certain semiconductors, including silicon, gallium arsenide, copper indium diselenide, and cadmium telluride, are uniquely suited to the photovoltaic conversion process.
semicrystalline--See 'Multicrystalline.'
series connection--A way of joining photovoltaic cells or batteries by connecting positive leads to negative leads; such a configuration increases the voltage.
series regulator--Type of battery charge regulator where the charging current is controlled by a switch, transistor, or FET connected in series with the PV module or array. As opposed to a shunt regulator, which gradually shorts out the panel output as the battery gets charged up.
series resistance--Parasitic resistance to current flow in a cell due to mechanisms such as resistance from the bulk of the semiconductor material, metallic contacts, and interconnections.
shelf life of batteries--The length of time, under specified conditions, that a battery can be stored so that it keeps its guaranteed capacity.
short-circuit current (Isc)--The current flowing freely from a photovoltaic cell through an external circuit that has no load or resistance; the maximum current possible.
shunt regulator--Type of a battery charge regulator where the charging current is controlled by a switch or transistor connected in parallel with the PV panel. Overcharging of the battery is prevented by shorting the PV output. Shunt regulators are common in PV systems as they are relatively cheap to build and simple to design. Series regulators usually have better control and charge characteristics. Most newer controllers have gone to series regulation.
silicon (Si)--A chemical element, atomic number 14, semi-metallic in nature, dark gray, an excellent semiconductor material. A common constituent of sand and quartz (as the oxide). Crystallizes in face-centered cubic lattice like a diamond. The most common semiconductor material used in making photovoltaic devices.
sine wave inverter--An inverter that produces utility-quality, sine wave power forms.
single-crystal material--A material that is composed of a single crystal or a few large crystals.
solar cell--See 'Photovoltaic cell.'
solar constant--The strength of sunlight; 1353 watts per square meter in space and about 1000 watts per square meter at sea level at the equator at solar noon. It increases at higher altitudes.
solar energy--Energy from the sun. The heat that builds up in your car when it is parked in the sun is an example of solar energy.
solar-grade silicon--Intermediate-grade silicon used in the manufacture of solar cells. Less expensive than electronic-grade silicon.
solar noon--That moment of the day that divides the daylight hours for that day exactly in half. To determine solar noon, calculate the length of the day from the time of sunset and sunrise and divide by two. Solar noon may be quite a bit different from 'clock' noon.
solar spectrum--The total distribution of electromagnetic radiation emanating from the sun.
solar thermal electric--Method of producing electricity from solar energy by using focused sunlight to heat a working fluid, which in turn drives a turbogenerator.
split-spectrum cell--A compound photovoltaic device in which sunlight is first divided into spectral regions by optical means. Each region is then directed to a different photovoltaic cell optimized for converting that portion of the spectrum into electricity. Such a device achieves significantly greater overall conversion of incident sunlight into electricity. See 'mulitjunction device.'
square wave inverter--The inverter consists of a dc source, four switches, and the load. The switches are power semiconductors that can carry a large current and withstand a high voltage rating. The switches are turned on and off at a correct sequence, at a certain frequency. The square wave inverter is the simplest and the least expensive to purchase, but it produces the lowest quality of power.
stand-alone (PV system)--An autonomous or hybrid photovoltaic system not connected to a grid. May or may not have storage, but most stand-alone systems require batteries or some other form of storage.
stand-off mounting--Technique for mounting a PV array on a sloped roof, which involves mounting the modules a short distance above the pitched roof and tilting them to the optimum angle.
standard test conditions (STC)--Conditions under which a module is typically tested in a laboratory: (1) Irradiance intensity of 1000 W/square meter (0.645 watts per square inch), AM1.5 solar reference spectrum, and (3) a cell (module) temperature of 25 degrees C, plus or minus 2 degrees C (77 degrees F, plus or minus 3.6 degrees F). [IEC 1215]
state of charge (SOC)--The available capacity remaining in the battery, expressed as a percentage of the rated capacity.
substrate--The physical material upon which a photovoltaic cell is made.
sulfation--A condition that afflicts unused and discharged batteries; large crystals of lead sulfate grow on the plate, instead of the usual tiny crystals, making the battery extremely difficult to recharge.
superstrate--The covering on the sun side of a PV module, providing protection for the PV materials from impact and environmental degradation while allowing maximum transmission of the appropriate wavelengths of the solar spectrum.
thermal electric--Electric energy derived from heat energy, usually by heating a working fluid, which drives a turbogenerator. See 'solar thermal electric.'
thermophotovoltaic (TPV) device--A device that converts secondary thermal radiation, re-emitted by an absorber or heat source, into electricity; The device is designed for maximum efficiency at the wavelength of the secondary radiation.
thick-crystalline materials--Semiconductor material, typically measuring from 200-400 microns thick, that is cut from ingots or ribbons.
thin film--A layer of semiconductor material, such as copper indium diselenide, cadmium telluride, gallium arsenide, or amorphous silicon, a few microns or less in thickness, used to make photovoltaic cells. Commonly called amorphous.
total internal reflection--The trapping of light by refraction and reflection at critical angles inside a semiconductor device so that it cannot escape the device and must eventually be absorbed by the semiconductor.
tracking array--PV array that follows the path of the sun to maximize the solar radiation incident on the PV surface. The two most common orientations are (1) one axis where the array tracks the sun east to west and (2) two-axis tracking where the array points directly at the sun at all times. Tracking arrays use both the direct and diffuse sunlight. Two-axis tracking arrays capture the maximum possible daily energy. Typically, a single axis tracker will give you 15% to 25% more power per day, and dual axis tracking will add about 5% to that. Depends somewhat on latitude and season.
transformer--Steps AC voltage up or down, depending on the application.
trickle charge--A charge at a low rate, balancing through self-discharge losses, to maintain a cell or battery in a fully charged condition.
two-axis tracking--A system capable of rotating independently about two axes (e.g., vertical and horizontal) and following the sun for maximum efficiency of the solar array.
utility-interactive inverter--An inverter that can function only when tied to the utility grid, and uses the prevailing line-voltage frequency on the utility line as a control parameter to ensure that the PV system's output is fully synchronized with the utility power.
VAC--Volts ac
VDC--Volts dc
Vmp--Voltage at maximum power
Voc--Open-circuit voltage
volt (V)--A unit of measure of the force, or 'push,' given the electrons in an electric circuit. One volt produces one ampere of current when acting a resistance of one ohm.
voltage at maximum power (Vmp)--The voltage at which maximum power is available from a module. [UL 1703]
wafer--A thin sheet of semiconductor material made by mechanically sawing it from a single-crystal or multicrystal ingot or casting.
watt (W)--The unit of electric power, or amount of work (J), done in a unit of time. One ampere of current flowing at a potential of one volt produces one watt of power.
watt-hour (Wh)--See 'Kilowatt-hour.'
waveform--The shape of the curve graphically representing the change in the ac signal voltage and current amplitude, with respect to time.